Give a few examples of active and passive immunity. Journal Articles on This Topic.
 3 Differences Of Active And Passive Vaccination Download Table
3 Differences Of Active And Passive Vaccination Download Table
Passive immunization should be considered when vaccines for active immunization are unavailable or contraindicated or in certain instances when unimmunized individuals have been exposed to the infective agent and require immediate protection.
Active vs passive immunization. Unlike vaccination however passive immunization and immunotherapy do not result in immunological memory. In addition to being imparted via a different means passive immunity is also not as durable as active immunity. Unlike vaccination however passive immunization and immunotherapy do not result in immunological memory.
Ziel einer solchen Simultanimpfung ist es einen schnell einsetzenden Sofortschutz durch die passive Immunisierung und eine lang anhaltende Immunität durch die aktive Immunisierung zu erreichen. Die zeitgleiche aktive und passive Impfung wird beispielsweise bei Tetanus- und. Protection is immediate whereas active immunity takes time usually several weeks to develop.
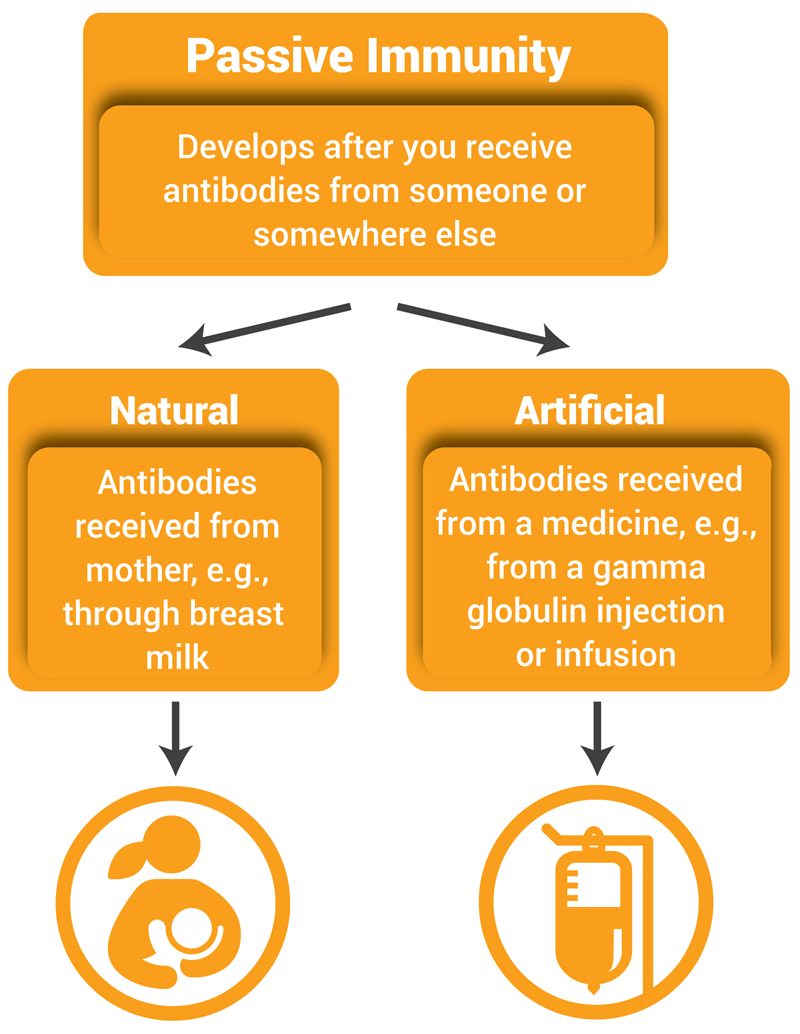
Passive immunization is where pre-synthesized elements of the immune system are transferred to a person so that the body does not need to produce these elements itself. A prominent difference between active and passive immunity is that active immunity is developed due to the production of antibodies in ones own body while passive immunity is developed by antibodies that are produced outside and then introduced into the body. What is passive immunity.
Active Immunization The goal of active immunization is to elicit protective immunity and immunologic memory. This method of immunization begins to work very quickly but it is short lasting because the antibodies are naturally broken down and if there. Immunization of chickenpox hepatitis flu and polio are some examples of active.
Active vs passive immunity Breast milk Injection Mother to baby through the placenta. Sie erfolgt nämlich nicht als präventive Schutzmaßnahme vor einer Krankheit sondern wird als sofortige Behandlungsmöglichkeit einer bestehenden Infektion eingesetzt. Active immunity and passive immunity are two types of adaptive immunity.
Theres active immunization and passive immunization. A successful active immunization elicits a heightened immune response after subsequent exposure to the pathogenic agent which help to eliminates the pathogen or prevents disease mediated by its products. In combined active-passive immunization adsorbed tetanus toxoid produced a significantly higher response than.
Active immunization is when we give you a vaccine and your immune system kicks into high gear and sets up a series of reactions in your body to trick your body into thinking that youve actually had the disease. The protection they provide lasts for a comparatively short amount of time. This is the major advantage to passive immunity.
Currently antibodies can be used for passive immunization. The protection they provide lasts for a comparatively short amount of time. Personnel were grouped according to conditions and duration of service and analyses were performed based on maximum and minimum hepatitis A projected incidences for each group.
Passive immunity can occur naturally when maternal antibodies are transferred to the fetus through the placenta and it can also be induced artificially when high levels of antibodies specific to a pathogen or toxin are transferred to non-immune persons through blood products that contain antibodies such as in immunoglobulin therapy or antiserum therapy. Only active immunity is long-lasting. Passive immunity is the transfer of active humoral immunity of ready-made antibodies.
Anders als bei der aktiven Immunisierung handelt es sich bei der passiven Immunisierung nicht um eine klassische Impfung. Passive immunization is when you get those pre-formed antibodies. We compared cost-benefit and cost-effectiveness analyses of hepatitis A prevention with immune serum globulin ISG vs inactivated hepatitis A vaccine iHAV in the Israel Defence Forces.
Active immunization can be achieved by. Passive immunity is when youre given antibodies as opposed to producing them on your own. Passive immunization also works quickly providing protection within hours or days whereas vaccines can take weeks or months if boosting more than one injection is required.
Aktive und passive Immunisierung lassen sich auch kombinieren. In the case of passive immunity protection is immediate. Active immunization utilizes an immunogen to generate a host response designed to eliminate the malignant cells whereas in passive immunization preformed antibodies or cells are administered to directly eliminate the transformed cells - examples of.
Passive immunization also works quickly providing protection within hours or days whereas vaccines can take weeks or months if boosting more than one injection is required. Active immunity takes place when the host produces antibodies when exposed to pathogens or bacteria while passive immunity takes place when the host receives antibodies from another source. However passive immunity lasts only for a few weeks or months.
Combined active-passive immunization with tetanus toxoid and 50 units TIGH gives a low level of passive immunity and stimulates early onset of active immunization. This form of protection from a pathogen dissipates over time says Eugene Oltz.
These methods expose your immune system to a type of germ or pathogen in vaccinations just a small. Once a microbe penetrates the bodys skin mucous membranes or other primary defenses it interacts with the immune system.
Passive Naturally Acquired Immunity.

Natural active immunity definition. Rats are highly resistant to diphtheria whereas unimmunized children readily contract the disease. Naturally Acquired Immunity Active Naturally Acquired Immunity. Natural immunity is a genetic characteristic of an individual and is due to the particular species and race to which one belongs to ones sex and to ones individual ability to produce immune bodies.
Natural immunity is a general and non-specific resistance to infection possessed by all healthy individuals. Vaccines provide artificial active immunity. Biology the ability of an organism to resist disease either through the activities of specialized blood cells or antibodies produced by them in response to natural exposure or inoculation active immunity or by the injection of antiserum or the transfer of antibodies from a mother to her baby via the placenta or breast milk passive immunity.
Active naturally acquired immunity refers to the natural exposure to an infectious. Natural immunity definition immunity that is present without prior immunization. B-cells in the body produce antibodies.
Males are more resistant to some disorders than are females and vice versa. This type of immunity is natural because deliberate exposure does not induce it. Definition of active immunity.
The primary response when a microorganism enters the body is described as natural active immunity. Natural immunity The ability to resist infection that does not depend on prior experience of the invading organism and the resultant production of antibodies or amendment or selection of LYMPHOCYTES. Active immunity definition.
There are two examples of passive naturally acquired immunity. Immunity that is naturally existing Natural immunity does not require prior sensitization to an antigen. Immunity possessed by a group as a species or race that is present in an individual at birth prior to exposure to a pathogen or antigen and that includes components as intact skin salivary enzymes neutrophils natural killer cells and complement which provide an initial response against infection called also natural immunity.
Naturally acquired active immunity occurs when a person is exposed to a live pathogen and develops a primary immune response which leads to immunological memory. Active immunity is the most common type. Active immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease.
CONTINUE SCROLLING OR CLICK HERE. Naturally acquired active immunity occurs when the person is exposed to a live pathogen develops the disease and becomes immune as a result of the primary immune response. The chickenpox vaccine is safer than a chickenpox party.
Infectious disease - Infectious disease - Natural and acquired immunity. Usually long-lasting immunity that is acquired through production of antibodies within the organism in response to the presence of antigens compare passive immunity Examples of active immunity in a Sentence. Persons of one race.
Chickenpox in adults is more severe. It develops in response to an infection or vaccination. Exposure to the disease organism can occur through infection with the actual disease resulting in natural immunity or introduction of a killed or weakened form of the disease organism through vaccination vaccine.
Every animal species possesses some natural resistance to disease. Also known as natural resistance. This is how people resisted disease for centuries before vaccines began to be consistently developed in the 1800s and widely distributed in the 1900s.
All humans are immune to certain diseases that affect animals of the lower species. Humans have a high degree of resistance to foot-and-mouth disease for example while the cattle and sheep with which they may be in close contact suffer in the thousands from it. The immune system naturally develops resistance to a disease after being infected although immunity occurs at varying levels depending upon the individual and the disease.
Signs of chickenpox include blisters rash and fever. Natural immunity - immunity to disease that occurs as part of an individuals natural biologic makeup innate immunity immunity resistance - medicine the condition in which an organism can resist disease. Chickenpox deaths are possible though rare.
The situation in which the body produces its own antibodies substances in the blood that.