The mass number symbol A from the German word Atomgewicht atomic weight also called atomic mass number or nucleon number is the total number of protons and neutrons together known as nucleons in an atomic nucleus. The mass of an atom or molecule on a scale where the mass of a carbon-12 12 C atom is exactly 120.
 Unit Iii The Atom And The Prediodic Table 2
Unit Iii The Atom And The Prediodic Table 2
In 1911 Ernest Rutherford gave a model of the atom in which a central nucleus held most of the atoms mass and a positive charge which in units of the electrons charge was to be approximately equal to half of the atoms atomic weight expressed in.
Atomic weight is equal to. The actual mass of an atom should be equal to. However an atomic weight equality relates to the mass of an element. The mass of any atom is approximately equal to the total number of its protons and neutrons multiplied by the atomic mass unit u 1660539 10 -24 gram.
Atomic weight is used to calculate the number of neutrons in an atom of an element. The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom of an element. Thus atoms must have equal numbers of protons and electrons.
Atomic weight is the relative weight of the atom on the basis of oxygen as 16. What does the mass number tell us. Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass about 167 10 -24 grams which scientists define as one atomic mass unit AMU.
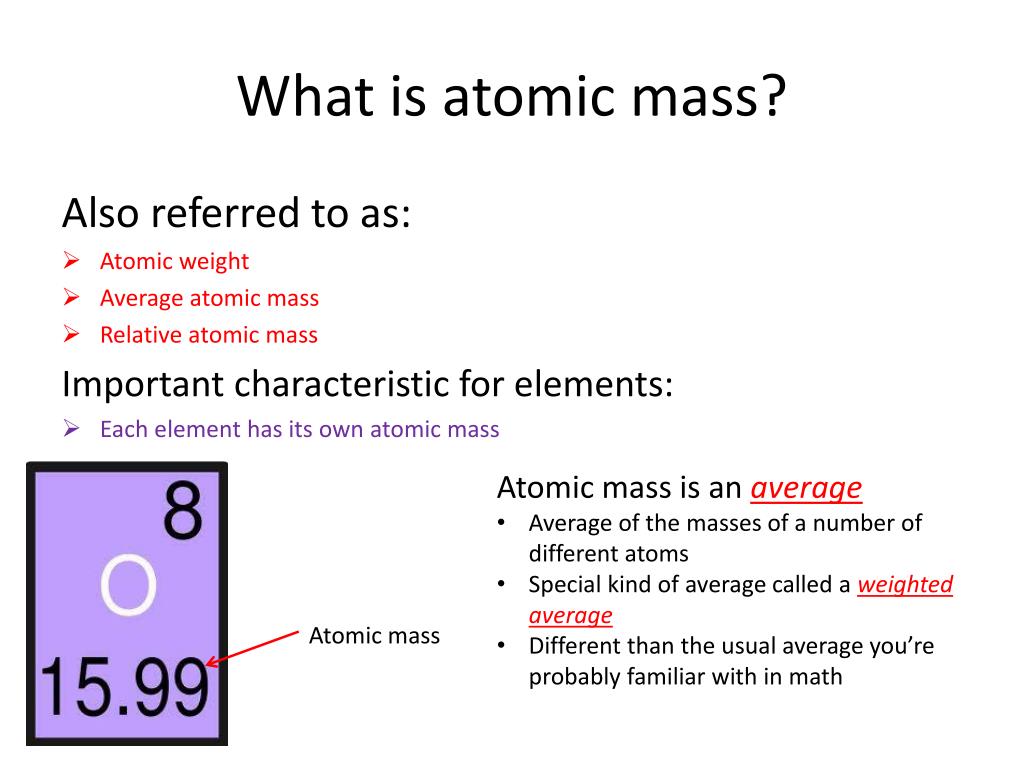
121 Zeilen Atomic weight also called relative atomic mass ratio of the average mass of a chemical element s atoms to some standard. In this case you use the atomic mass in calculations rather than the atomic weight of the element from the. The atomic mass or weighted average of hydrogen is around 1008 amu.
These weights expressed in grams are called gram atomic weights. To determine the most abundant isotopic form of an element compare given isotopes to the weighted average on the periodic table. An isotope is one of two or more species of atoms of the same chemical element that have different atomic mass.
The total weight of an atom is called the atomic weight. Atoms are electrically neutral. Therefore the atomic mass average of the element that is mentioned in the problem should occupy the numerical position on the right side of an atomic weight equality.
For example the three hydrogen isotopes in Figure PageIndex1 are H-1 H-2 and H-3. Electrons are much lighter about 00005486 u. Molar mass edit The molar mass of a substance is the mass of 1 mole of that substance in multiples of the gram.
That means that there must be a balance between the positively charged protons and the negatively charged electrons. The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an atoms nucleus. Atomic Mass and Mass Number 1 The mass in the amu of the electron proton and neutron is fractional.
The atomic mass is the sum of the mass of protons and neutrons. It is approximately equal to the number of protons and neutrons with a little extra added by the electrons. 2 Due to the mass loss of the nucleus the actual mass of an atom is slightly less than the sum of the mass of electron.
For a pure isotope the atomic weight rounded off to the nearest integer gives the total number of neutrons and protons making up the atomic nucleus. 1 its ATOMIC WEIGHT is equal to the weight of the PROTON - 1 2 its ELECTRON is so light in weight that its weight doesnt matter 3 sometimes when a HYDROGEN atom has 1 NEUTRON it has a weight of 2 1 PROTON 1 NEUTRON. Hence the correct option is D.
3 The atomic weights of. This example is from Wikipedia and may be reused under a CC BY-SA license. Copper has a density of 894 gcm and an atomic weight of 63546 gmol so there are molm.
Since 1961 the standard unit of atomic mass has been one-twelfth the mass of an atom of the isotope carbon-12. Atomic mass and atomic weight may equal each other whenever you are working with a single isotope of an element too. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted mass of all the naturally presented isotopes on earth.
Equivalent weight has the dimensions and units of mass unlike atomic weight which is dimensionless. The mass of 1 mole of a substance is equal to its relative atomic or molecular mass in grams. The number of neutrons is equal to the atomic weight minus the atomic number the number of protons.
The stability of the nucleus and hence the atoms radioactivity is heavily dependent upon the number of neutrons it contains.