An isotope that is radioactive is called a radioisotope orradionuclide. The most stable isotope of uranium U-238 has an atomic number of 92 protons and an atomic weight of 238 92 protons plus 146 neutrons.
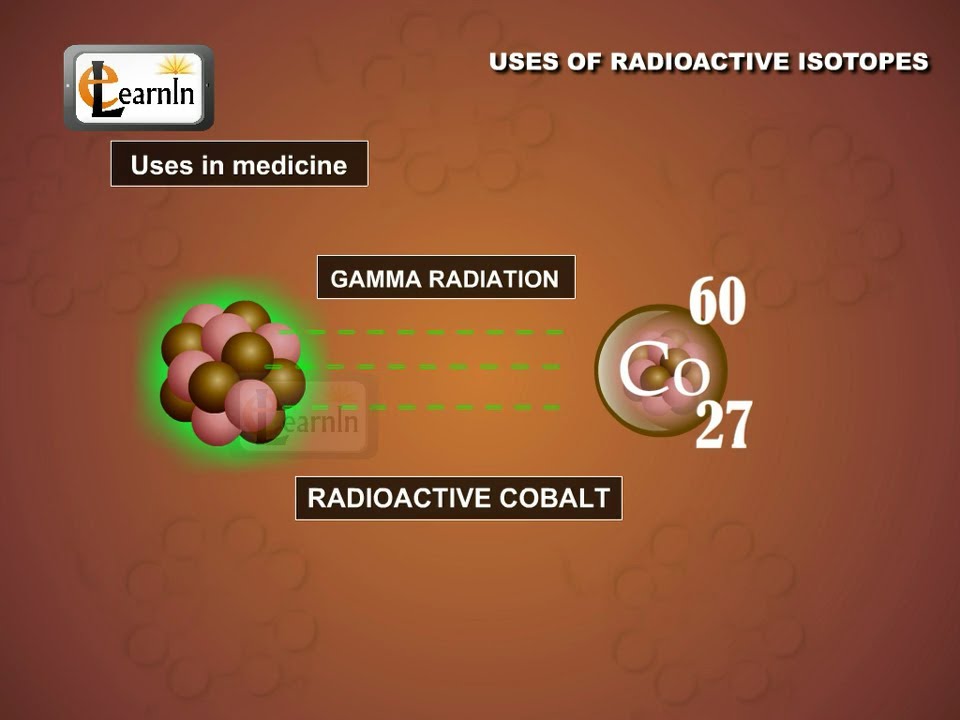 Uses Of Radioactive Isotopes Chemistry Youtube
Uses Of Radioactive Isotopes Chemistry Youtube
Radioactive primordial and stable isotopes Some isotopesnuclides are radioactive and are therefore referred to as radioisotopes or radionuclides whereas others have never been observed to decay radioactively and are referred to as stable isotopes or stable nuclides.

What is an radioactive isotope. Such nuclei decompose spontaneously by emission of a nuclear electron β particle or helium nucleus α particle and radiation γ rays thus achieving a stable nuclear composition. Isotopes are samples of an element with different numbers of neutrons in their atoms. Radioactive Isotope Marine Life.
A radioactive isotope is an isotope of an element radiating during its decay to a stable form. Radioactivity is the property of some unstable atoms radionuclides to spontaneously emit nuclear radiation usually alpha particles or beta particles often accompanied by gamma-raysThis radiation is emitted when the nucleus undergoes radioactive decay and is converted into a different isotope which may according to its number of neutrons and protons be either radioactive unstable. Synthetic radioisotope is a radioisotope that is formed and made by humans.
The energy liberated in the form change can be measured with a Geiger counter or with photographic film. The number of protons for different isotopes of an element does not change. Radionuclides eg cesium are released from weapon testing and use and from industrial accidents such.
All isotopes have the same number of protons however different isotopes may have differing numbers of neutrons. An isotope with an unstable nuclear composition. April 28 2013.
Synthetic radioactive isotopes are generated from the use of nuclear energy for peaceful and military purposes. Occurrence of Radioactive Elements in. Primordial radionuclides originate in the geosphere and anthropogenic radionuclides are.
Table of Radioactive Isotopes LBNL Isotopes Project - LUNDS Universitet Disaster Preparedness for Radiology Professionals American College of Radiology ACR 2006Some of these radionuclides are packaged in shielded housings with sample volumes in the mm 3 to cm 3 range and used as illumination sources for imaging or therapeutic purposes. Scientists create artificial. Radioisotope also known as radisotope These are radioactive isotopes since they have an unstable atomic nucleus due to the balance between neutrons and protons and emit energy and particles when it changes to a more stable form.
Radioactive tracers usually emit gamma rays which can easily pass through the tissues in the patients body to detectors outside the body. Two examples may help clarify this. The first step in an isotope scan is to transfer the isotope into the body.
Not all isotopes are radioactive. Radioactive isotopes can be used in medical imaging. Below we will discuss the number of radioactive isotopes due to nuclear power generation as well as nuclear experiments.
The radioisotope known as the radioactive tracer is given to the patient by injection inhalation or orally through the mouth. An isotope having an unstable nucleus that decomposes spontaneously by emission of a nuclear electron or helium nucleus and radiation thus achieving a stable nuclear composition. Used as tracers and as radiation and energy sources.
These may occur naturally as in the cases of radium and uranium or may be created artificially. This is done a variety of ways which include injection into a vein inhalation or drinking a liquid that contains the isotope. Stable isotopes either never decay or else decay.
Radioisotope rade-o-iso-tōp a radioactive form of an element consisting of atoms with unstable nuclei which undergo radioactive decay to stable forms emitting characteristic alpha beta or gamma radiation. Learn the basics about radioactive isotopesThe identity and chemical properties of any atom are determined by the number of protons in its nucleus.