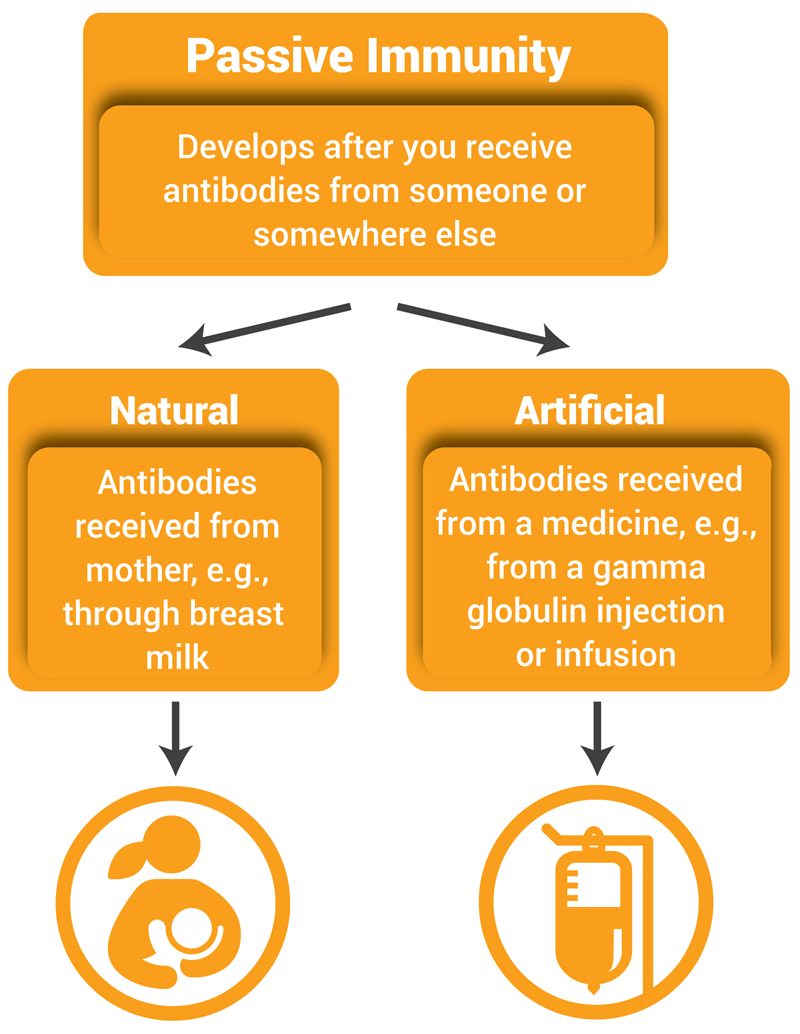
A newborn baby acquires passive immunity from its mother through the placenta. Maternal passive immunity or natural passive immunity is immunity passed along from mother to child.
 Active Vs Passive Immunity Smaller Itr Laboratories Canada Inc
Active Vs Passive Immunity Smaller Itr Laboratories Canada Inc
And Google dictionary states that this acquired immunity is from either the development of antibodies as a response to antigen exposure 1 from vaccination or 2 an attack.

Active immunity and passive immunity. Unlike active immunity passive immunity is. This is an example of passive immunity because it artificially exposes. Role of phagocytes in innate or nonspecific immunity.
This may occur naturally for example the transfer of antibodies across the placenta from a mother to her baby or artificially for example the administration of human immunoglobulin to non-immune pregnant women who have been in contact with chickenpox. Active immunity occurs naturally in a person while passive immunity is triggered by an external force. View Full Document.
Active immunity is the immune response to a pathogen. Passive And Active Immunity Research 327 Words 2 Pages. Passive immunity is acquired when antibodies are introduced into the body from an external source usually through.
Two different categories of our immune system are. Explain the difference between passive and active immunity. Passive immunity involves the transfer of preformed antibodies from an immune individual to a non immune one.
In both cases the protection. Passive immunity is provided when a person is given antibodies to a disease rather than producing them through his or her own immune system. Artificial means such as injection of antibodies or Vaccines.
B lymphocytes B cells Self vs. Passive immunization is used when there is a high risk of infection and insufficient time for the body to develop its own immune response or to reduce the symptoms of ongoing or immunosuppressive diseases. Innate and adaptive humoral vs.
In the below section of this report we have mentioned some evident differences between active vs passive immunity. Active Immunity Passive Immunity. Types of immune responses.
What is Active Immunity. Antibodies and acquired immunity. In addition to being imparted via a different means passive immunity is also not as durable as active immunity.
The ebook Focus on Pharmacology explains on page 114 that the active immunity is acquired immunity. Active immunity is immunity that develops as a result of natural or deliberate exposure to an antigen. This leads to the production of antibodies in the body.
A vaccination is an example of active immunity. In each case immunity can be acquired either by 1. Passive immunity is when youre given antibodies as opposed to producing them on your own.
The process by which the organisms immune capacity is developed by gradually introducing the antigens in a very minimal amount is termed as active immunity. Artificial passive immunity comes from injected antibodies created within a. Active immunity requires something to trigger a response which is produced from an individuals immune system.
Passive immunity is the transfer of active humoral immunity in the form of ready-made antibodies from one individual to another. Inactive immunity the individual itself produces the antibodies to. The immune system then produces B and T cells that quicken and strengthen the bodys response to repeated infection.
Passive immunity Vaccines provide active immunity against the disease Active immunity Education and informed consent should be obtained by physician Acquired immunity By getting the disease and fighting it off you have passive immunity from the antibodies Roles of vaccines versus acquired immunity ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Therapeutic Procedure A1. This form of protection from a. Active and passive immunity.
Active immunity is long-lasting and sometimes life-long. While active immunity occurs when an individual produces antibodies to a disease through his or her own immune system passive immunity is provided when a person is given antibodies. Passive immunity occurs when antibodies are introduced rather than made eg from breast milk or antisera.
After birth an infant continues to receive passive immunity to disease from antibodies found in breast milk. Active immunity is attained by exposure to a pathogen. Active and passive immunity vaccine types excipients and licensing Abstract Immunity is the state of protection against infectious disease conferred either through an immune response generated by immunization or previous infection or by other non-immunological factors.
It relies on the body making antibodies which take time to mount an attack against bacteria or viruses. The immune response occurs immediately. Ensuing are important points that explain and distinguish active and passive immunity.
Immunity to infectious microorganisms can be achieved by active or passive immunization. Natural processes usually by transfer from mother to fetus or by previous infection by the organism 2. Vaccinations stimulate the immune system with an antigen.
Before the child is born antibodies are passed through the placenta to protect the child from illness. In the case of passive immunity protection is immediate.
These methods expose your immune system to a type of germ or pathogen in vaccinations just a small. Once a microbe penetrates the bodys skin mucous membranes or other primary defenses it interacts with the immune system.
Passive Naturally Acquired Immunity.

Natural active immunity definition. Rats are highly resistant to diphtheria whereas unimmunized children readily contract the disease. Naturally Acquired Immunity Active Naturally Acquired Immunity. Natural immunity is a genetic characteristic of an individual and is due to the particular species and race to which one belongs to ones sex and to ones individual ability to produce immune bodies.
Natural immunity is a general and non-specific resistance to infection possessed by all healthy individuals. Vaccines provide artificial active immunity. Biology the ability of an organism to resist disease either through the activities of specialized blood cells or antibodies produced by them in response to natural exposure or inoculation active immunity or by the injection of antiserum or the transfer of antibodies from a mother to her baby via the placenta or breast milk passive immunity.
Active naturally acquired immunity refers to the natural exposure to an infectious. Natural immunity definition immunity that is present without prior immunization. B-cells in the body produce antibodies.
Males are more resistant to some disorders than are females and vice versa. This type of immunity is natural because deliberate exposure does not induce it. Definition of active immunity.
The primary response when a microorganism enters the body is described as natural active immunity. Natural immunity The ability to resist infection that does not depend on prior experience of the invading organism and the resultant production of antibodies or amendment or selection of LYMPHOCYTES. Active immunity definition.
There are two examples of passive naturally acquired immunity. Immunity that is naturally existing Natural immunity does not require prior sensitization to an antigen. Immunity possessed by a group as a species or race that is present in an individual at birth prior to exposure to a pathogen or antigen and that includes components as intact skin salivary enzymes neutrophils natural killer cells and complement which provide an initial response against infection called also natural immunity.
Naturally acquired active immunity occurs when a person is exposed to a live pathogen and develops a primary immune response which leads to immunological memory. Active immunity is the most common type. Active immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease.
CONTINUE SCROLLING OR CLICK HERE. Naturally acquired active immunity occurs when the person is exposed to a live pathogen develops the disease and becomes immune as a result of the primary immune response. The chickenpox vaccine is safer than a chickenpox party.
Infectious disease - Infectious disease - Natural and acquired immunity. Usually long-lasting immunity that is acquired through production of antibodies within the organism in response to the presence of antigens compare passive immunity Examples of active immunity in a Sentence. Persons of one race.
Chickenpox in adults is more severe. It develops in response to an infection or vaccination. Exposure to the disease organism can occur through infection with the actual disease resulting in natural immunity or introduction of a killed or weakened form of the disease organism through vaccination vaccine.
Every animal species possesses some natural resistance to disease. Also known as natural resistance. This is how people resisted disease for centuries before vaccines began to be consistently developed in the 1800s and widely distributed in the 1900s.
All humans are immune to certain diseases that affect animals of the lower species. Humans have a high degree of resistance to foot-and-mouth disease for example while the cattle and sheep with which they may be in close contact suffer in the thousands from it. The immune system naturally develops resistance to a disease after being infected although immunity occurs at varying levels depending upon the individual and the disease.
Signs of chickenpox include blisters rash and fever. Natural immunity - immunity to disease that occurs as part of an individuals natural biologic makeup innate immunity immunity resistance - medicine the condition in which an organism can resist disease. Chickenpox deaths are possible though rare.
The situation in which the body produces its own antibodies substances in the blood that.